Study identifies genetic tendency in leukemia cells
Scientists have identified a way of predicting early whether patients will develop a common type of leukemia, based on their genetics.
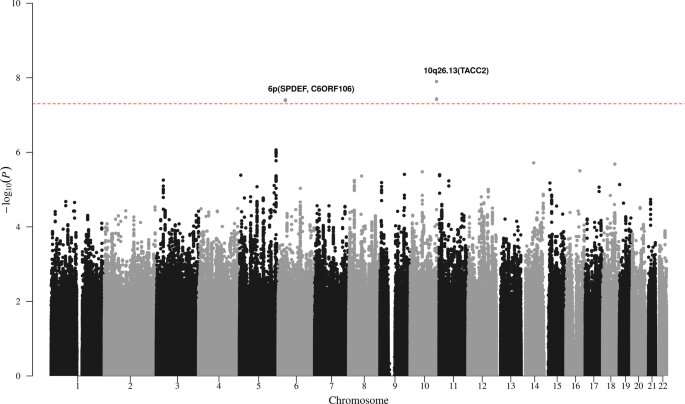
Newcastle University co-led the study, published in Nature Communications, that focused on the most common type of blood cancer: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL).
By examining blood samples of patients with CLL, experts discovered that there was a genetic tendency to develop progressive forms of the illness in some patients.
The study presents the opportunity in future to warn prospective patients that they also possess the genetic make-up that could lead to developing progressive CLL and design a personalized treatment process for them long before the illness takes effect.
Professor James Allan, from Newcastle University Centre for Cancer, said: “Emerging evidence suggests that early treatment for patients at high-risk of developing progressive CLL could significantly delay the onset of symptomatic Leukemia and improve survival.
“The results from this collaborative study will help patients and their doctors make important decisions about when to start treatment.”
CLL varies in its severity amongst patients; while some develop symptoms such as weight loss and lumps in the neck and armpits, others exhibit no symptoms at all, despite the leukemia cells being present within their blood.
Dr. David Allsup, Senior Lecturer at Hull York Medical School, University of Hull, said: “The study has demonstrated that CLL patients often possess the same genetic tendencies, and as such we can analyze the non-cancerous cells of prospective patients to predict the likelihood of future diagnosis.
“The study also allows us to move towards a more personalized diagnosis of leukemia and adapt our approach for patients based on the likelihood of them developing aggressive symptoms.”
While this discovery does not constitute a cure for the disease, it goes a long way in identifying it in patients early, and thereby increasing their chances of survival.
Source: Read Full Article



