A new phenotype of LRP6 mutation
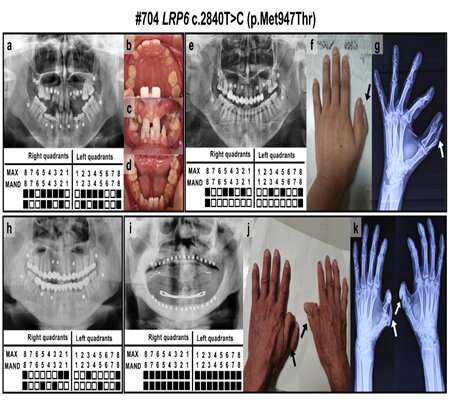
A group led by Prof. Han Dong of Peking University School of Stomatology reported for the first time hand preaxial polydactyly in patients with tooth agenesis carrying a previously unknown mutation of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6). The study was published November 10 in NPJ Genomic Medicine.
In the study, the researchers performed whole-exome sequencing and clinical assessment of three families with inherited tooth agenesis to investigate the genetic causes and clinical phenotypes, and reported (1) a rare phenotype of hand preaxial polydactyly in a tooth agenesis family with an unreported autosomal dominant LRP6 heterozygous mutation (c.2840 T > C;p.Met947Thr) and (2) another unreported autosomal dominant LRP6 heterozygous mutation (c.1154 G > C;p.Arg385Pro) in a non-syndromic tooth agenesis family.
The findings enlarged the LRP6 mutation spectrum of tooth agenesis and broadened the phenotypic spectrum of LRP6-related disorders, which may help clinicians to differentiate diagnosis, target pathogenic genes in advance, and facilitate the genetic studies of tooth agenesis patients.
Prof. Han served as corresponding author of the paper, and Dr. Zhang Liutao from the 2021 Class of the school’s integrated 8-year MD/Ph.D. program and Assistant Fellow Yu Miao were first authors.
The research group on developmental dental anomalies at Peking University was initiated by Prof. Feng Hailan, and is currently led by Prof. Han. The group has long been devoted to research in the molecular mechanism of developmental dental anomalies and its clinical translation, and boasts the world’s biggest biobank and digital information database of tooth agenesis.
Source: Read Full Article



