What is an Ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a type of oscillating sound pressure wave that has a higher frequency than human hearing is able to detect. Ultrasound is not a unique type of sound, therefore, but is classified differently due to the fact that humans cannot hear it. Ultrasound has a frequency greater than 20kHZ, which is beyond the frequency limit of sounds that humans are able to hear.
In 1794, Lazzaro Spallanzani demonstrated that bats did not rely on vision but, rather, utilized the echo of a type of sound that was inaudible to the human ear to navigate their path. This later led to further research in the field and eventually led to the concept of ultrasound that we know now.
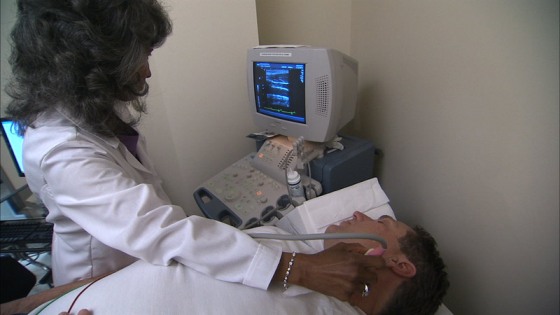
Medical Uses
Ultrasound has proven to be useful in many fields including medical imaging, which is also referred to as sonography. The technique is utilized by veterinarians and medical practitioners and offers a way to scan for objects and measure distances in living bodies.
The concept of using high frequency sound waves for medical optical imaging was first penned in 1939 by Sokolov, although the initial images produced were low quality in terms of contrast and sensitivity.
Over the following years, the technique was tweaked such that ultrasonography is has been used in medical practices as a tool to visualize muscles, tendons, internal organs and tumors for more than 50 years. It is widely known for its use in prenatal care, with its ability to visualize and monitor the growth of a growing fetus during pregnancy.
Ultrasonography offers many tangible benefits, including:
- Portable devices
- Cost-effective
- Non-destructive nature
Given these benefits, ultrasound is becoming increasingly common in emergency medicine to visualize internal issues quickly and help in emergency decision-making.
Industrial Uses
There are several practical uses of ultrasound in various different industries, including helping in the process of cleaning and accelerating chemical reactions.
Ultrasonic impact treatment focuses ultrasonic energy toward metals to manipulate its properties, such as grain refinement and size.
Ultrasonication is a form of liquid or slurry procession that enhances the incorporation of substances of chemical reactions on an industrial level. Exposure leads to cavitation, which involves the formation and collapse of several small vacuum bubbles, which helps to keep mixtures smooth and uniform.
Ultrasonic standing waves can also be used to trap particular fibers, which has proved useful in the paper industry. It enables a simple system to measure fibers and produce paper with fibers oriented using the sound waves.
Ultrasonic cleaning is often used to clean jewelry, optical lenses, dental and surgical instruments and some industrial parts. The energy released as the sound waves hit the surface of the object to be cleaned creates bubbles by cavitation and directs tiny jets towards the surfaces, providing the cleaning action. This technique can also be directed towards surfaces infected with bacteria to kill related particles.
Uses for Animals
Some animals, such as bats and porpoises, rely on ultrasound to locate nearby prey or obstacles. Their hearing spectrum differs from that of humans and can detect ultrasound wave frequencies. They emit sounds in the ultrasound frequency and are receptive to the way in which the sound reflects back to them, as it bounces off from surrounding objects.
Many insects are also able to detect ultrasonic waves and use this ability to escape from their predators – like bats – when they hear them emitting sounds. Other animals that can detect ultrasound waves include dogs, cats, whales and dolphins.
References
- https://web.archive.org/web/20070221101616/http://www.aium.org/patient/aboutexam/safety.asp
- http://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=genus
- http://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/ultrasound/basics/definition/prc-20020341
- http://www.fda.gov/radiation-emittingproducts/radiationemittingproductsandprocedures/ucm115357.htm
Further Reading
- All Ultrasound Content
- Ultrasound Therapeutic Applications
- Ultrasound scans – is there a difference between 3D and 4D scans?
- What is Transvaginal Ultrasound?
- Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Uses
Last Updated: Aug 23, 2018

Written by
Yolanda Smith
Yolanda graduated with a Bachelor of Pharmacy at the University of South Australia and has experience working in both Australia and Italy. She is passionate about how medicine, diet and lifestyle affect our health and enjoys helping people understand this. In her spare time she loves to explore the world and learn about new cultures and languages.
Source: Read Full Article



