A network that spreads light in our brain and the role of the thalamus
New research conducted at the University of Liège, using ultra-high field 7 Tesla MRI, provides a better understanding of how light stimulates our brain and could provide new insights into how it works.
A research team at the ULiège GIGA Institute tried to understand better how light stimulates our cognition. Light acts like a cup of coffee and helps keep us awake. That’s why we recommend not using too much light on our smartphones and tablets in the evening. This can disrupt our sleep.
On the other hand, the same light can help us during the day. Many studies have shown that good lighting can help students in schools, hospital staff and patients, and company employees. It’s the blue part of the light that’s most effective for this, as we have blue light detectors in our eyes that tell our brains about the quality and quantity of light around us.
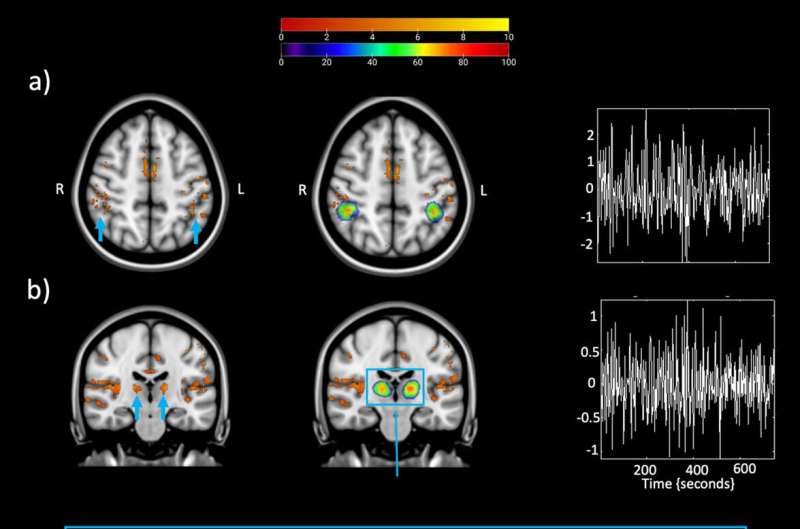
Once again, the brain regions responsible for this stimulating impact of light (also known as the “non-visual” impact of light) are not well understood. “They are small and located in the subcortical part of the brain,” explains Ilenia Paparella, doctoral student in the GIGA CRC IVI laboratory and first author of the article published in Communications Biology.
The team of researchers from the GIGA-CRC-IVI was once again able to take advantage of the higher resolution of 7 Tesla MRI to show that the thalamus, a subcortical region located just below the corpus callosum (that connects our two hemispheres), plays a role in relaying non-visual light information to the parietal cortex in an area known to control attention levels.
“We knew of its important role in vision, but its role in non-visual aspects was not yet certain. With this study, we have demonstrated that the thalamus stimulates the parietal regions and not the other way around, as we might have thought.”
These new advances in our knowledge of the role of the thalamus will ultimately enable us to propose lighting solutions that will help cognition when we need to be fully awake and focused, or that will contribute to better sleep through relaxing light.
More information:
Ilenia Paparella et al, Light modulates task-dependent thalamo-cortical connectivity during an auditory attentional task, Communications Biology (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s42003-023-05337-5
Journal information:
Communications Biology
Source: Read Full Article



